All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The Lymphoma Hub uses cookies on this website. They help us give you the best online experience. By continuing to use our website without changing your cookie settings, you agree to our use of cookies in accordance with our updated Cookie Policy
Introducing

Now you can personalise
your Lymphoma Hub experience!
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View content recommended for you
Find out moreThe Lymphoma Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the Lymphoma Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The Lymphoma Hub and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
TARMAC trial: Time-limited ibrutinib plus CAR T-cell therapy for the treatment of R/R MCL
Bookmark this article
Patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) experience high response rates with CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells; however, there is a risk of relapse and often considerable toxicity.
Here, we summarize the outcomes of the phase II TARMAC (NCT04234061) trial, published by Minson et al.1 in Blood, of the combination of time-limited ibrutinib and CTL019 CAR T-cells in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Study methods1
- This ongoing phase II study included patients with R/R MCL after ≥1 prior line of therapy.
- Ibrutinib was started at least 7 days before leukapheresis and continued through CAR T-cell production for at least 6 months after CAR T-cell administration.
- The primary endpoint was complete response (CR) rate at Month 4 after CAR T-cell infusion.
- Secondary endpoints included safety, overall response rate, measurable residual disease (MRD) negativity at Months 1, 4, 6, 9, and 12, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival; responses were also analyzed based on TP53 mutation status.
Key findings1
- Overall, 20 patients were included in the study:
- 75% were male;
- the median age was 66 years;
- The median time from study enrollment to CAR T-cell infusion and CAR T-cell manufacture was 60 days and 49 days, respectively; and
- 50% of patients had prior Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) exposure and 45% were BTKi refractory, with 15% receiving >1 BTKi.
- After infusion, the 4-month endpoint of CR rate was high, with a similar overall response rate, and an MRD-negativity rate of 70% (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Response to treatment*
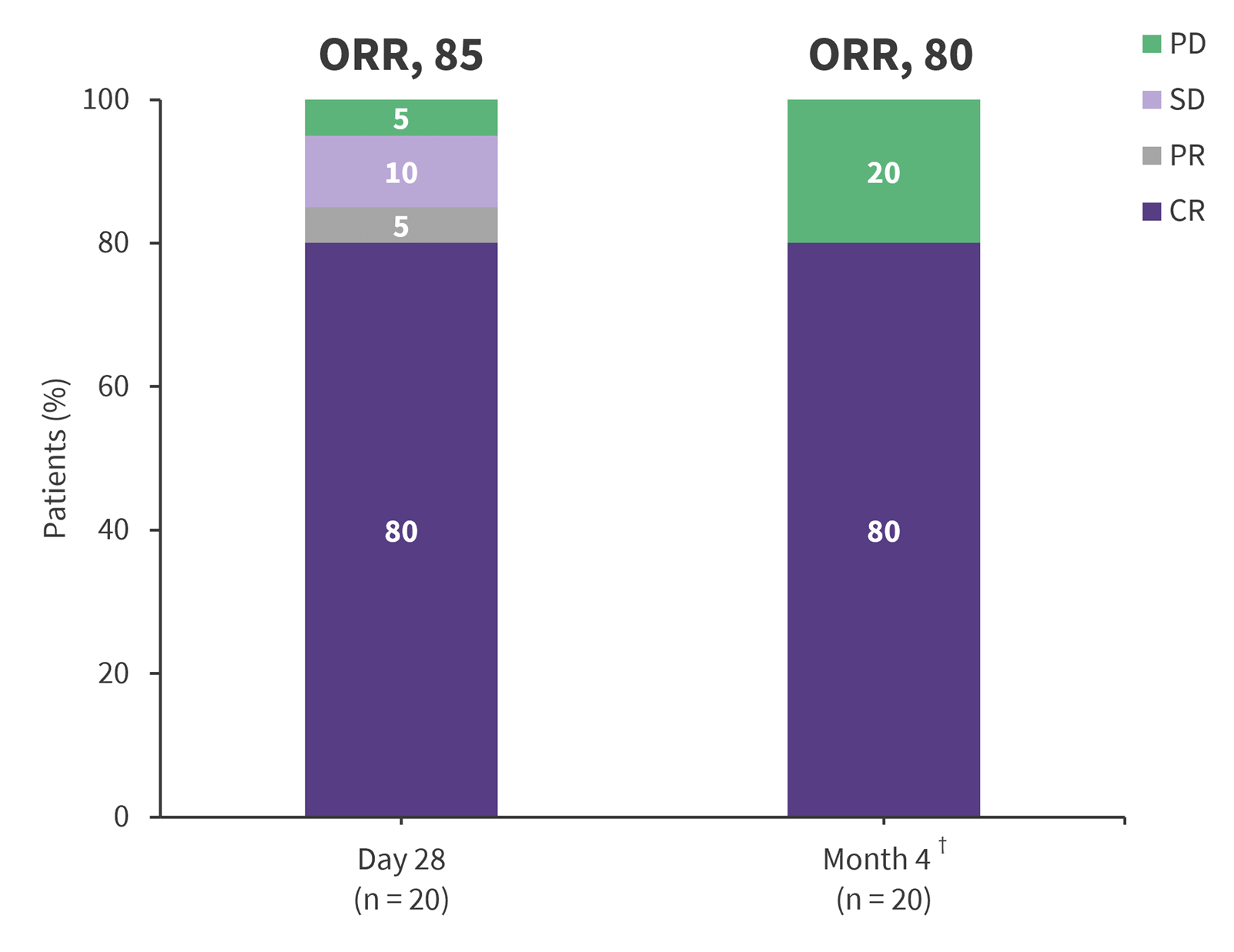
CR, complete response; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease.
*Adapted from Minson, et al.1
†14 patients were MRD negative by flow cytometry.
- At the median follow-up of 13 months, median PFS was not reached; however, the estimated 12-month PFS and overall survival were 75% and 100%, respectively.
- Deep and durable responses were seen in high-risk subgroups, including in patients with prior BTKi exposure or TP53 mutation.
- Deep responses were associated with robust CAR T-cell expansion and a less exhausted baseline T-cell phenotype.
- All patients reported an adverse event of any grade:
- 15 patients developed CRS (Grade 1–2, n = 12; Grade 3, n = 3).
Two patients developed reversible Grade 1–2 neurotoxicity.
| Key learnings |
|
- Minson A, Hamad N, Cheah CY, et al. CAR T cells and time-limited ibrutinib as treatment for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: the phase 2 TARMAC study. Blood 2024;143(8):673-684. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2023021306

Understanding your specialty helps us to deliver the most relevant and engaging content.
Please spare a moment to share yours.
Please select or type your specialty
 Thank you
Thank youRelated articles
Newsletter
Subscribe to get the best content related to lymphoma & CLL delivered to your inbox








